S h a r e
EV charging sockets explained


Posted by
Kevin Blackmore
August 2023
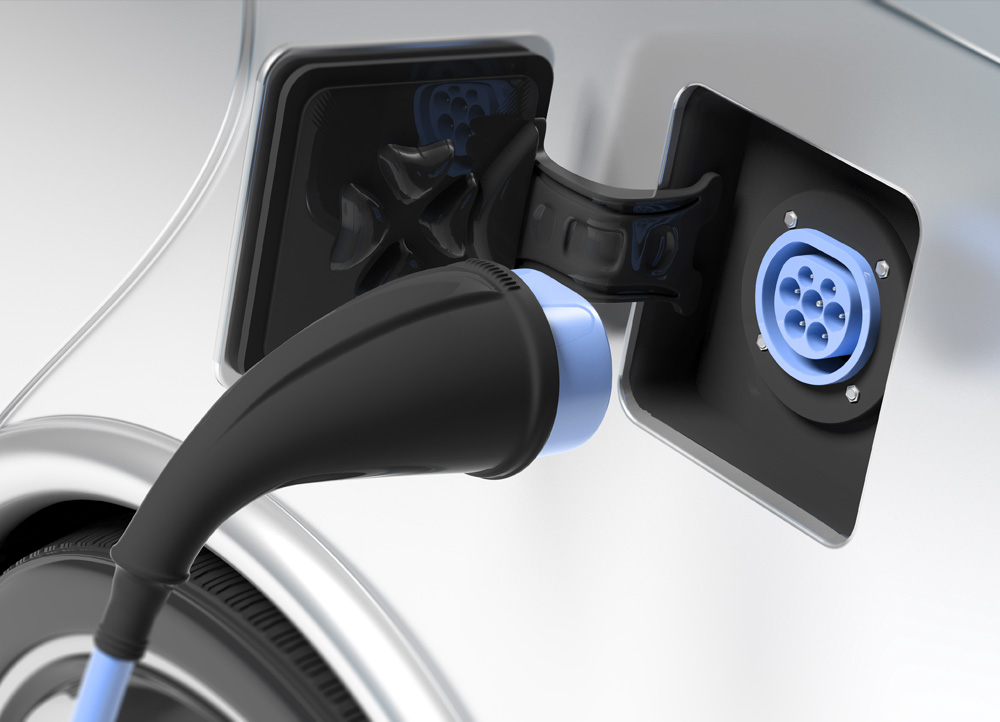
When it comes to charging an electric vehicle, there are two connectors (plugs and sockets) to consider – the connector on the vehicle, and the connector on the charge point you plan to use.
There are two types of connector for electric vehicles when using slow or fast alternating current (AC) charging – though one of these systems has a huge majority. This is the Type 2 connector, the European standard for many years now, though some older EVs in the UK will have a Type 1 connector.
The same is true for rapid or ultra-rapid direct current (DC) charging, with two main connector types, one of which is dominant. CCS connectors are most likely to be found on an electric vehicle that’s capable of rapid charging, though some have CHAdeMO connectors.
Generally speaking, most slow and fast charge points have a Type 2 socket, whereas DC rapid and ultra-rapid charge points – the latter also known as high-power chargers – have cables attached so there’s no socket on the charge point side.
Portable charging cables are available that match the vehicle’s connector type, allowing drivers to charge their electric vehicle on the go.
This guide is split into two sections:
- Vehicle socket types – the different types of sockets you might find on the car itself.
- Charge point socket types – the different types of sockets you might find on charge points at home, at work or on-the-go.
Vehicle socket types
Vehicles are fitted with up to two charging sockets. For single-socket cars, Type 2 tends to be most popular. Type 2 is the standard socket type throughout Europe meaning you can charge just about any car from it. Where two sockets are fitted to allow rapid charging, your car will feature a combination of Type 1 and CHAdeMO sockets, or the combined Type 2 CCS socket.
Slow and fast charging
Slow and fast charging utilises AC and are generally used to charge vehicles at home, at work, or at “destinations”. There are two main vehicle connector types:
Type 1
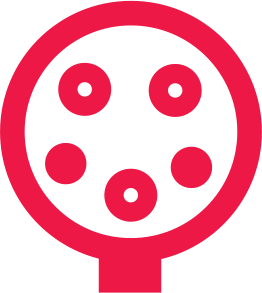
Typical power ratings: 3.7kW (12.5 miles range per charge hour) and 7kW (25 miles range per charge hour). Type 1 connectors are the standard in the US and are single-phase only.
Type 2

Typical power ratings: 3.7kW (12.5 miles range per charge hour), 7kW (25 miles range per charge hour) and 22kW (three-phase) (75 miles range per charge hour). Type 2 connectors are the European standard. Only Type 2 connectors support three-phase power. However, three-phase power is rare in the UK at domestic properties.
Rapid charging
Rapid charging is typically used for topping up on-the-go. There are two main vehicle connector types:
CHAdeMO

Typical power rating: Used on first generation Renault Zoe models, as well as initial Tesla Supercharger units, output varied from 43kW to around 130kW. Renault now uses CCS for those with rapid charging capability, and Tesla has added CCS to its models, so Type 2 is rarely used for any rapid charging anymore – either AC or DC.
CCS (Combined Charging System)
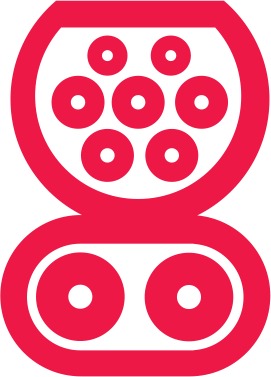
Typical power rating: 50kW (75 miles range per half hour charge). 350kW chargers exist offering 525 miles range per half-hour charge. In addition, 150kW rapid chargers are gradually being introduced however, these are rare. CSS supports higher power output than CHAdeMO and for this reason, is likely to eventually replace CHAdeMO as the UK standard.
Type 2

Typical power rating: Used on first generation Renault Zoe models, as well as initial Tesla Supercharger units, output varied from 43kW to around 130kW. Renault now uses CCS for those with rapid charging capability, and Tesla has added CCS to its models, so Type 2 is rarely used for any rapid charging anymore – either AC or DC.
Chargepoint socket types
Slow and fast charging – AC
Type 2 is the standard charge point socket type for home, work, and destination charging. At home, a standard 3 pin plug can also be used in emergencies.
Type 2

Typical power ratings: 7kW (25 miles range per charge hour) and 22kW (three-phase) (75 miles range per charge hour). Type 2 connectors are a universal socket requiring the driver to plug in their own cable in order to charge.
Domestic 3-pin

Typical power rating: 2.3kW (8 miles range per charge hour). Low power rating makes charging slow. Should only be used if no other charging solution is available.
Type 1
Some charge points – often legacy units – have Type 1 tethered (attached) connectors available, though these are increasingly few and far between. Most public points are untethered Type 2 points, to allow any type of EV to charge should the driver have the cable, which they usually will.
Rapid chargers – DC
Rapid chargers have cables attached to the units, so there’s rarely a socket on the unit. Some points will have a Type 2 AC socket for drivers, but primarily, they will use one, two, or three cables tethered to the point. This is because the cables are larger and heavier to deal with higher power ratings, and saves drivers carrying a bulky cable and connector about with them.

